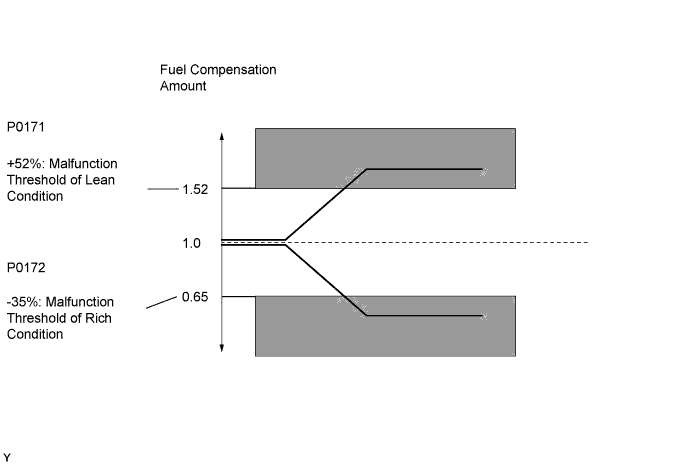
DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) |
DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1) |
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0171 | With warm engine and stable air fuel ratio feedback, fuel trim considerably in error to lean side (2 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0172 | With warm engine and stable air fuel ratio feedback, fuel trim considerably in error to rich side (2 trip detection logic). |
|
| 1.CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0171 OR P0172) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| DTC P0171 or P0172 is output | A |
| DTC P0171 or P0172 and other DTCs are output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK PCV HOSE CONNECTIONS |
Inspect the PCV hose connections (Click here).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM |
Check the intake system for vacuum leaks (Click here).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME FOR A/F SENSOR) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) (Click here).
Start the engine.
Warm up the engine and run the engine at an engine speed of 2500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor / All Data / AFS Voltage B1S1 and O2S B1S2.
Perform the Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor operation with the engine idling (press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
Monitor the voltage outputs of the air fuel ratio sensor and the heated oxygen sensor (AFS Voltage B1S1 and O2S B1S2) displayed on the tester.
| Tester Display (Sensor) | Injection Volume | Status | Voltage |
| AFS Voltage B1S1 (Air fuel ratio) | 12.5% | Rich | Less than 3.1 V |
| -12.5% | Lean | Higher than 3.4 V | |
| O2S B1S2 (Heated oxygen) | 12.5% | Rich | Higher than 0.55 V |
| -12.5% | Lean | Less than 0.4 V |
| Status AFS Voltage B1S1 | Status O2S B1S2 | Air Fuel Ratio Condition and Air Fuel Ratio Sensor Condition | Suspected Trouble Area | Proceed to |
| Lean/Rich | Lean/Rich | Normal | - | A |
| Lean | Lean | Actual air fuel ratio lean |
| A |
| Rich | Rich | Actual air fuel ratio rich |
| A |
| Lean | Lean/Rich | Air fuel ratio sensor malfunction |
| B |
| Rich | Lean/Rich | Air fuel ratio sensor malfunction |
| B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 5.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (COOLANT TEMP) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Coolant Temp.
Read the Coolant Temp twice, when the engine is both cold and warmed up.
| Tester Display | Condition | Specified Condition |
| Coolant Temp | Cold engine | Same as ambient air temperature |
| Warm engine | Between 75 and 100°C (167 and 212°F) |
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 6.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MAF) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Put the engine in inspection mode (maintenance mode) (Click here).
Start the engine.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / MAF, Coolant Temp and Engine Speed.
Allow the engine to idle until Coolant Temp reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
Read MAF with the engine speed at 2500 rpm.
| Tester Display | Condition | Specified Condition |
| MAF | Park (P) has been selected A/C: off Engine Speed: 2500 rpm | Between 4.5 gm/sec. and 8.5 gm/sec. |
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 7.CHECK FUEL PRESSURE |
Check the fuel pressure (Click here).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 8.INSPECT FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK |
Inspect for exhaust gas leaks.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 9.CHECK FOR SPARK (SPARK TEST) |
Perform a spark test (Click here).
| NEXT | |
| 10.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (INJECTION AND VOLUME) |
Check the injection and volume.
| Result | Proceed to |
| NG | A |
| OK | B |
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||
| 11.INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE) |
Inspect the air fuel ratio sensor (Click here).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 12.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (POWER SOURCE OF AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR) |
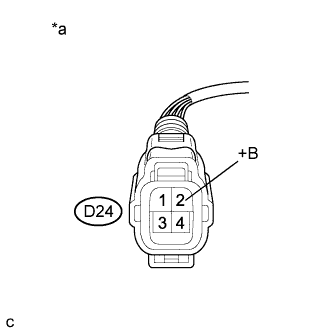 |
Disconnect the air fuel ratio sensor connector.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
| Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
| D24-2 (+B) - Body ground | Power switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| *a | Front view of wire harness connector (to Air Fuel Ratio Sensor) |
Reconnect the air fuel ratio sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 13.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the air fuel ratio sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| D24-1 (HA1A) - D28-18 (HA1A) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| D24-3 (A1A+) - D28-103 (A1A+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| D24-4 (A1A-) - D28-126 (A1A-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| D24-1 (HA1A) or D28-18 (HA1A) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| D24-3 (A1A+) or D28-103 (A1A+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| D24-4 (A1A-) or D28-126 (A1A-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Reconnect the air fuel ratio sensor connector.
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 14.REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
Replace the air fuel ratio sensor (Click here).
| NEXT | |
| 15.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0171 OR P0172) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
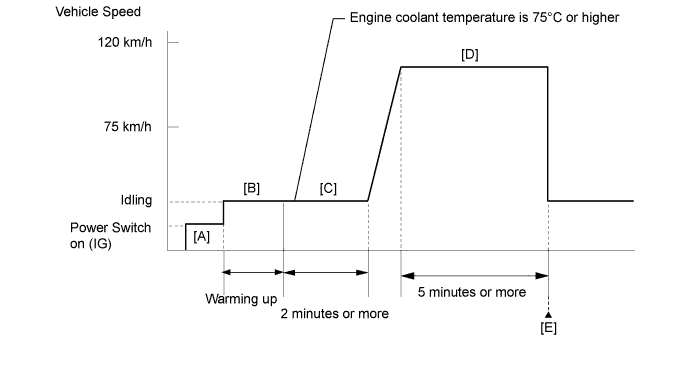
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC / Pending.
Read the pending DTCs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| DTC P0171 or P0172 is output | A |
| DTC is not output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 16.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER SUB-ASSEMBLY CONNECTOR CONNECTION) |
Check the connection and terminal contact pressure of connectors and wire harnesses between the mass air flow meter sub-assembly and ECM (Click here).
| NEXT | |
| 17.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0171 OR P0172) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC / Pending.
Read the pending DTCs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| DTC P0171 or P0172 is output | A |
| DTC is not output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 18.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER SUB-ASSEMBLY - ECM) |
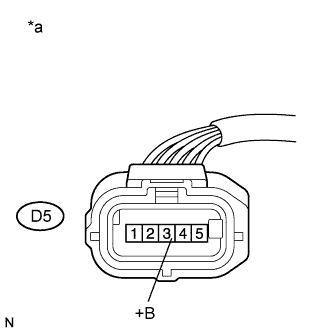 |
Disconnect the mass air flow meter sub-assembly connector.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
| Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
| D5-3 (+B) - Body ground | Power switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| *a | Front view of wire harness connector (to Mass Air Flow Meter Sub-assembly) |
Reconnect the mass air flow meter sub-assembly connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 19.REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER SUB-ASSEMBLY |
Replace the mass air flow meter sub-assembly (Click here).
| NEXT | |
| 20.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the power switch on (IG).
Turn the tester on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in the Confirmation Driving Pattern.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC / Pending.
Read the pending DTCs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| DTC is not output | A |
| DTC P0171 or P0172 is output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||